We Use CookiesWe use cookies to enhance the security, performance,
functionality and for analytical and promotional activities. By continuing to browse this site you
are agreeing to our privacy policy
10 Best Magnifying Glass
From leading brands and best sellers available on the web.By clicking on a link to a third party's website, log data is shared with that third party.
Buying Guide for the Best Magnifying Glass
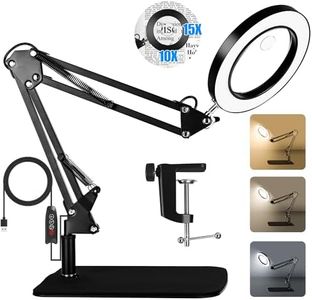
Choosing the right magnifying glass can make a big difference in comfort, effectiveness, and enjoyment, whether you're using it for reading, hobbies, crafts, or inspection. The key is to consider how and where you'll use the magnifier, then select features that match your specific needs. This means looking at things like magnification strength, lens size, lens material, handle design, and portability. Understanding these features will help you make a smart choice that fits your goals.Magnification PowerMagnification power is a measure of how much larger the magnifying glass makes objects appear compared to their real size. It’s usually expressed as '2x', '5x', and so on. This is one of the most important specs because it directly affects how much detail you'll see. Low powers like 2x or 3x are good for general reading and scanning larger areas because they offer a wide, clear view. Mid-range powers (4x-7x) are great for more detail, like seeing stamps or coins, but with a slightly smaller viewing area. High powers (8x and above) let you see very small details but the viewing area shrinks and it becomes harder to keep things in focus. To pick the right one, think about your main task: choose lower power for reading or crafts, and higher power for inspecting tiny objects.
Lens DiameterLens diameter refers to the physical size of the magnifying glass's lens, usually measured in millimeters or inches. A larger lens lets you see more area at once, making it easier to read entire lines of text or view bigger objects without moving the glass around. Smaller lenses are more portable and can be more effective at higher magnifications. If your main goal is reading books, newspapers, or inspecting medium-sized items, a bigger lens is better. For detail work or for carrying in your pocket, a smaller diameter is often more convenient.
Lens MaterialThe lens on a magnifying glass is typically made from either glass or plastic (acrylic). Glass lenses usually provide clearer, more accurate images and are more scratch-resistant but can be heavier and may break if dropped. Plastic or acrylic lenses are lighter and less likely to shatter, though they may scratch more easily and sometimes produce minor distortions. If you want durability and are rough on your tools, or you want something lighter for carrying around, plastic is suitable. For best optical clarity, glass is the preferred option.
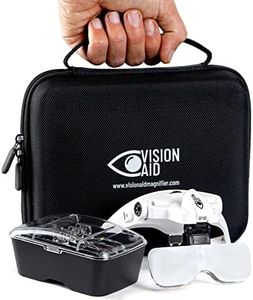
LightingSome magnifying glasses come with built-in lighting, usually LEDs, to help illuminate whatever you're looking at. Lighting can make a big difference in low-light conditions or when working with fine details. If you expect to use your magnifier in dim environments or need to see very small or low-contrast items, consider one with built-in lights. For use in bright places, lighting might not be as important.
Handle Design and ErgonomicsThe handle is what you'll be holding, and its design affects comfort during use. Handles can be long, short, padded, or shaped for a firmer grip. If you'll use the magnifier for longer periods, look for one with a comfortable, ergonomic handle to reduce hand fatigue. If you need to carry it easily or use it occasionally, a simpler, smaller handle may suffice. Try to imagine how you'll hold and use it in real situations.
PortabilityPortability relates to the size, weight, and design of the magnifying glass, affecting how easy it is to take with you. Pocket magnifiers fold up or come with cases and are ideal for travel. Bigger stationary models are best kept at home or on a workbench. Choose a more portable model if you plan to take your magnifier on the go frequently, otherwise, comfort and ease of use for home or desk work might be more important.