We Use CookiesWe use cookies to enhance the security, performance,
functionality and for analytical and promotional activities. By continuing to browse this site you
are agreeing to our privacy policy
10 Best Soldering Irons
From leading brands and best sellers available on the web.By clicking on a link to a third party's website, log data is shared with that third party.
Buying Guide for the Best Soldering Irons
Selecting the right soldering iron can make your electronics, crafting, or repair projects much easier and safer. It's important to think about what you'll be using your soldering iron for most often, as different jobs might need very different features or power levels. You should also consider your experience level, as some irons are geared toward beginners, while others are better suited for more advanced users. Getting familiar with key specifications will help you find a soldering iron that matches your needs and provides consistent, reliable performance.WattageWattage measures how much power the soldering iron can deliver, affecting how quickly it heats up and how well it can maintain temperature during use. For lighter tasks, like delicate electronics, irons in the 15-30 watt range are often enough, as they offer better control and lower risk of damage. For heavier work, such as soldering larger wires or stained glass, an iron with 40 watts or more is better since it can provide more heat. Think about what kinds of materials and components you'll work with most to choose the right wattage—higher isn't always better for fine jobs.
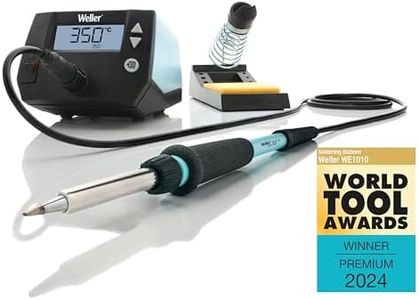
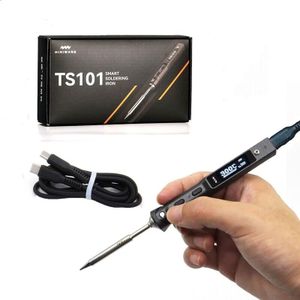
Temperature ControlTemperature control allows you to set and maintain a specific heat level, which can be crucial if you work with sensitive components or different types of solder. Some soldering irons have a fixed temperature, which is simpler to operate, while variable temperature models give you more flexibility for a wider range of projects. If you plan to tackle a variety of tasks, variable control is a good investment, but if you only need simple repairs now and then, a fixed temperature iron might be easier to use.
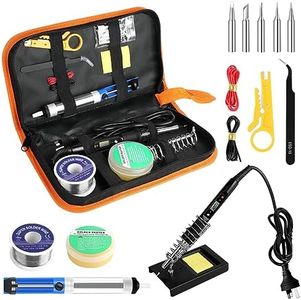
Tip Type and SizeThe tip of the soldering iron transfers heat to the work surface, and its size and shape make a big difference in how precisely you can work. Fine-point tips are ideal for small electronics or intricate work, while chisel or larger tips are better for bigger joints or tasks that need more heat transfer. Think about the size and detail of your typical projects—smaller, more delicate projects require finer tips, and larger jobs may benefit from broader ones.
Ergonomics and GripHow a soldering iron feels in your hand affects comfort and accuracy, especially during longer sessions. Look for models with comfortable, insulated handles that stay cool and are easy to hold for extended periods. Lightweight irons are easier to control and cause less fatigue. If you expect to do long or frequent soldering, a more comfortable grip will help avoid hand strain.
Heating TechnologySoldering irons use different heating methods, such as standard ceramic heaters or more advanced induction heating. Ceramic heaters are common and heat up quickly, making them suitable for most users. Induction heating gives faster response and very stable temperature, which can be useful for advanced or professional use. Consider your usage frequency and need for temperature accuracy when deciding if basic ceramic or advanced heating makes sense for you.
Safety FeaturesSafety features such as auto shut-off, heat-resistant stands, and insulated cords help prevent accidents and protect both you and your workspace. If you work in a shared area or might become distracted, these features are particularly helpful. Choose the features that match your habits—more safety features offer peace of mind for less experienced users or busy work areas.