We Use CookiesWe use cookies to enhance the security, performance,
functionality and for analytical and promotional activities. By continuing to browse this site you
are agreeing to our privacy policy
10 Best Automotive Wire Connectors
From leading brands and best sellers available on the web.By clicking on a link to a third party's website, log data is shared with that third party.
Buying Guide for the Best Automotive Wire Connectors
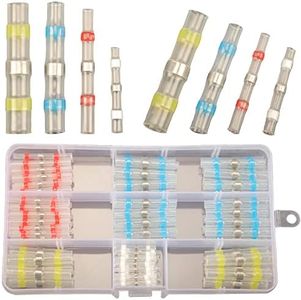
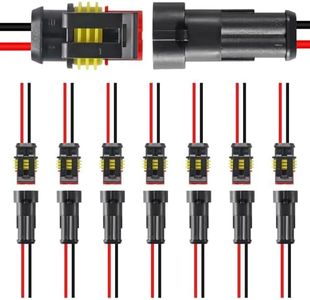
Choosing the right automotive wire connector is important to ensure that your vehicle’s electrical systems work reliably and safely. Whether you’re repairing a single wire or upgrading your whole wiring setup, you want connectors that fit well, handle the right amount of power, and last a long time under tough automotive conditions. Understanding the various specifications can help you select connectors that match your needs and avoid future electrical issues.Connector TypeConnector type simply refers to the style and design of how the wires join together. Popular types include butt connectors, spade terminals, ring terminals, and quick-disconnect connectors. Why does this matter? Different jobs need different connector types: for example, a ring terminal is ideal for grounding, while a quick-disconnect is great when you need to remove or replace components frequently. To pick the right one, think about how permanent the connection should be, what kind of access you'll need to the connection in the future, and what the original part was designed for.
Wire Gauge CompatibilityWire gauge compatibility tells you what thickness of wire the connector will safely accept. Wire size in vehicles is usually measured using the AWG (American Wire Gauge) standard, where smaller numbers mean thicker wire. It’s crucial to match the connector to your wire size so the connection is secure and carries current safely. Usually, connectors are labeled with a range, such as 22-18 AWG for thinner wires and 12-10 AWG for thicker ones. Choose connectors that match your wire size; using incompatible sizes can cause loose connections, overheating, or even electrical fires.
Current and Voltage RatingThe current and voltage rating describes how much electrical power a connector can handle without failing. Connectors designed for higher currents are usually larger and use stronger materials. Pay attention to these ratings: using a connector below the requirement can result in melted connectors or damaged circuits. To choose correctly, check the expected current and voltage for your application (for example, headlights draw more current than small sensors) and make sure your connectors exceed those limits for safety.
Weatherproofing (Sealing)Some connectors are labeled as weatherproof or sealed, meaning they’re built to keep out moisture, dirt, and other debris. This feature is especially important in areas of a vehicle exposed to the elements, like under the hood or near the wheels. Sealed connectors use rubber gaskets or other barriers to protect the wires and contacts. If your wiring will be exposed to rain, mud, or engine heat, weatherproof connectors are a wise choice. For inside-the-cabin or protected locations, standard non-sealed connectors are usually sufficient.
Material QualityThe material quality of both the connector body and the metal contact is critical for long-term performance. Connector housings are often made from plastic, nylon, or high-temperature materials, while the internal contacts are typically tin, copper, or brass. Higher quality materials resist corrosion, handle heat better, and make a better electrical connection. Opt for connectors with materials that match your environment—look for corrosion-resistant metals if you live where roads are salted or if moisture is a concern.
Connection Method (Crimp vs. Solder)How you secure the wire in the connector—whether you crimp (compress with a tool), solder, or use a screw-down method—affects the strength and reliability of the connection. Crimp connectors are fast and reliable when used with the right tool, and are popular for most automotive wiring. Soldered connections can be very strong and conductive but take more time and skill. If you value easy installation and reliable results, crimp connectors are a good general choice. If you need maximum strength in a non-vibrating location and have the skill, soldering may be the way to go.